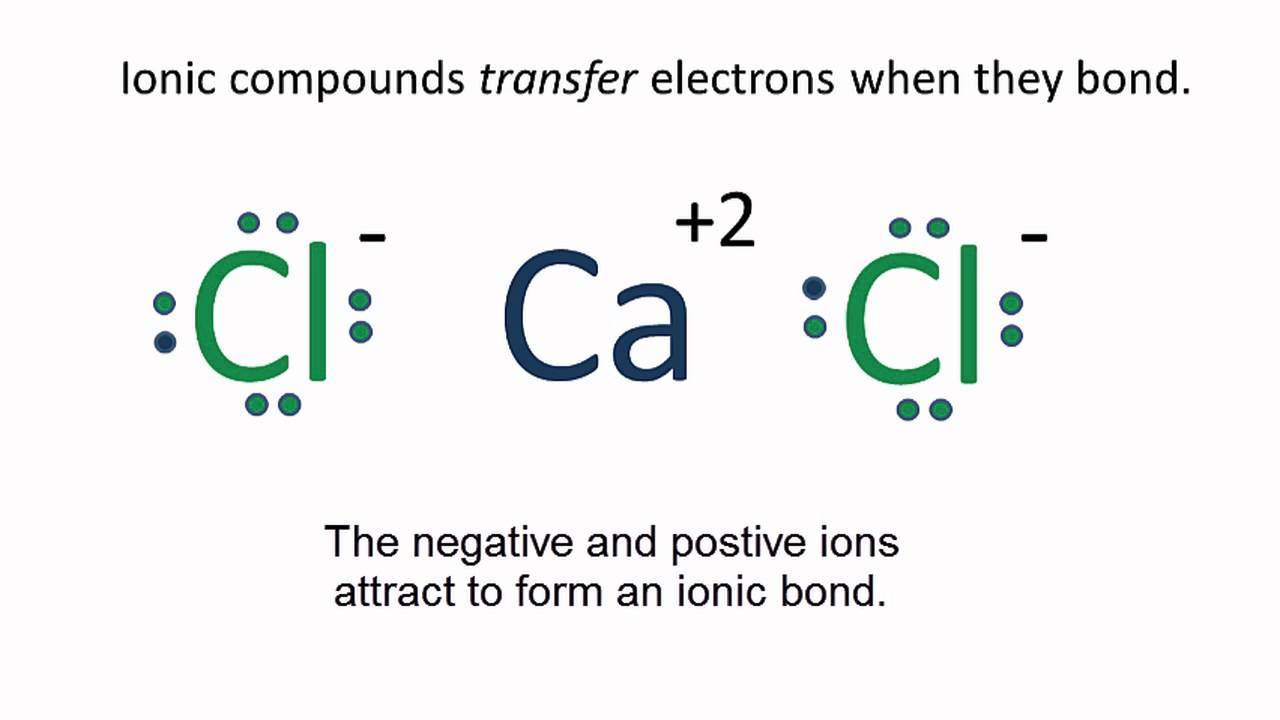
- Lewis Dot Structure Covalent Bonds
- Covalent Bonds Lewis Structures Worksheet
- Lewis Dot Structure Covalent Bonds Calculator Answer
- Lewis Structure Covalent Compound Calculator
- Lewis Dot Structure Covalent Bonds Calculator Present Value
- Covalent Lewis Dot Structure
- Covalent Bonds Lewis Dot Diagram
It is possible to draw a structure with a double bond between a boron atom and a fluorine atom in BF 3, satisfying the octet rule, but experimental evidence indicates the bond lengths are closer to that expected for B–F single bonds. This suggests the best Lewis structure has three B–F single bonds and an electron deficient boron. 1-3: Covalent Bonding and Lewis Dot Structures NOTES Chemical Bonds o Intramolecular force that holds 2 atoms together o 3 Types of Chemical Bonds: (1) Ionic (2) Metallic (3) Covalent – nonpolar and polar o GOAL OF BONDING: Sec. 1 The Covalent Bond o Form molecules (neutral group of atoms held together by covalent bonds). A Lewis structure is a graphic representation of the electron distribution around atoms. The reason for learning to draw Lewis structures is to predict the number and type of bonds that may be formed around an atom. A Lewis structure also helps to make a prediction about the geometry of a molecule.
Formal charge:
Let us draw the Lewis structure for carbon dioxide.
1. Skeletal structure
2. Total number of valence electrons in CO2
=[1 x 4(carbon)] +[2 x 6(oxygen)] = 4+ 12 = 16
3. Draw single bonds between atoms. Two bonds can be drawn as shown in the figure for CO2 which accounts for four electrons (2 bond pairs).
4. Distribute the remaining twelve electrons (16 - 4= 12) as six lone pairs starting from most electronegative atom, the oxygen. Six lone pairs are distributed to the two terminal oxygens (three each) to satisfy their octet.
Lewis Dot Structure Covalent Bonds
5. Verify weather all the atoms have octet configuration. In the above distribution, the central carbon has two pair short for octet. Therefore, to satisfy the octet rule two lone pairs from one oxygen or one pair from each oxygen can be moved to form multiple bonds, leading the formation of two possible structures for carbon dioxide as shown below
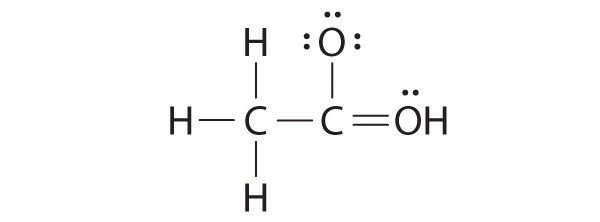
Similarly, the Lewis structure for many molecules drawn using the above steps gives more than one acceptable structure. Let us consider the above mentioned two structures of carbon dioxide.
Which one the above forms represents the best distribution of electrons in the molecule. To find an answer, we need to know the formal charge of each atom in the Lewis structures. Formal charge of an atom in a molecule, is the electrical charge difference between the valence electron in an isolated atom and the number of electrons assigned to that atom in the Lewis structure.
Where,
Nv- Number of valence electron of atom in its isolated state.
Nl - Number of electrons present as lone pairs around the atom in the Lewis structure
Nb - Number of electrons present in bonds around the atom (bond pairs) in the Lewis structure]
Now let us calculate the formal charge on all atoms in both structures,
For Structure 1,
For structure 2
Formal charge on carbon

After calculating the formal charges, the best representation of Lewis structure can be selected by using following guidelines.
1. A structure in which all formal charges are zero preferred over the one with charges.
2. A structure with small formal charges is preferred over the one with higher formal charges.
3. A structure in which negative formal charges are placed on the most electronegative atom is preferred.
In case of CO2 structures, the structure one is preferred over the structure 2 as it has zero formal charges for all atoms.
Covalent Bonds Lewis Structures Worksheet
Formal charge:
Let us draw the Lewis structure for carbon dioxide.
1. Skeletal structure
2. Total number of valence electrons in CO2
=[1 x 4(carbon)] +[2 x 6(oxygen)] = 4+ 12 = 16
3. Draw single bonds between atoms. Two bonds can be drawn as shown in the figure for CO2 which accounts for four electrons (2 bond pairs).
4. Distribute the remaining twelve electrons (16 - 4= 12) as six lone pairs starting from most electronegative atom, the oxygen. Six lone pairs are distributed to the two terminal oxygens (three each) to satisfy their octet.
Lewis Dot Structure Covalent Bonds Calculator Answer
5. Verify weather all the atoms have octet configuration. In the above distribution, the central carbon has two pair short for octet. Therefore, to satisfy the octet rule two lone pairs from one oxygen or one pair from each oxygen can be moved to form multiple bonds, leading the formation of two possible structures for carbon dioxide as shown below
Lewis Structure Covalent Compound Calculator
Similarly, the Lewis structure for many molecules drawn using the above steps gives more than one acceptable structure. Let us consider the above mentioned two structures of carbon dioxide.
Which one the above forms represents the best distribution of electrons in the molecule. To find an answer, we need to know the formal charge of each atom in the Lewis structures. Formal charge of an atom in a molecule, is the electrical charge difference between the valence electron in an isolated atom and the number of electrons assigned to that atom in the Lewis structure.
Where,
Nv- Number of valence electron of atom in its isolated state.
Nl - Number of electrons present as lone pairs around the atom in the Lewis structure
Nb - Number of electrons present in bonds around the atom (bond pairs) in the Lewis structure]
Now let us calculate the formal charge on all atoms in both structures,
For Structure 1,
Lewis Dot Structure Covalent Bonds Calculator Present Value
For structure 2
Formal charge on carbon
Covalent Lewis Dot Structure
After calculating the formal charges, the best representation of Lewis structure can be selected by using following guidelines.
1. A structure in which all formal charges are zero preferred over the one with charges.

Covalent Bonds Lewis Dot Diagram
2. A structure with small formal charges is preferred over the one with higher formal charges.
3. A structure in which negative formal charges are placed on the most electronegative atom is preferred.
In case of CO2 structures, the structure one is preferred over the structure 2 as it has zero formal charges for all atoms.